IOT
IoT, or the Internet of Things, refers to the network of physical objects, devices, vehicles, buildings, and other items that are embedded with sensors, software, and connectivity, allowing them to collect and exchange data over the internet. The IoT enables these objects to communicate with each other and with people, providing new ways to monitor, control, and optimize various systems and processes.The devices that make up the IoT are designed to collect and transmit data, and can be used in a wide range of industries, including healthcare, manufacturing, transportation, agriculture, and energy. For example, a smart thermostat in a home can use data from temperature sensors to adjust the heating and cooling system based on occupancy patterns and weather conditions, while a connected car can provide real-time information on traffic, fuel usage, and vehicle performance.The IoT relies on a range of technologies, including sensors, wireless networks, cloud computing, and data analytics. The data collected by IT devices can be analyzed to gain insights into patterns, trends, and anomalies, enabling organizations to make more informed decisions and improve their operations.While the IoT offers many benefits, it also raises concerns around privacy, security, and data ownership. As the number of connected devices continues to grow, these issues will need to be addressed to ensure that the IoT can be used safely and effectively. Our expertise with IoT development enables us to build IoT based secure applications addressing all the concerns expressed above.
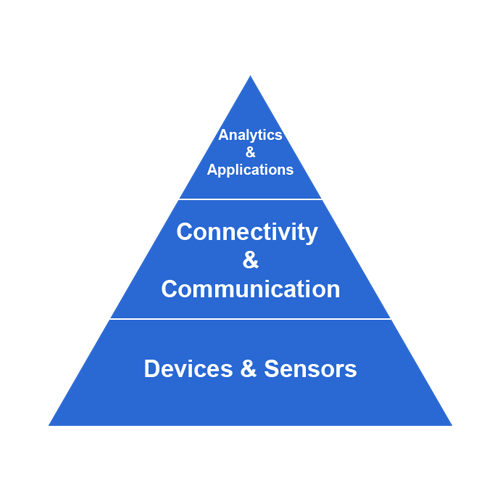
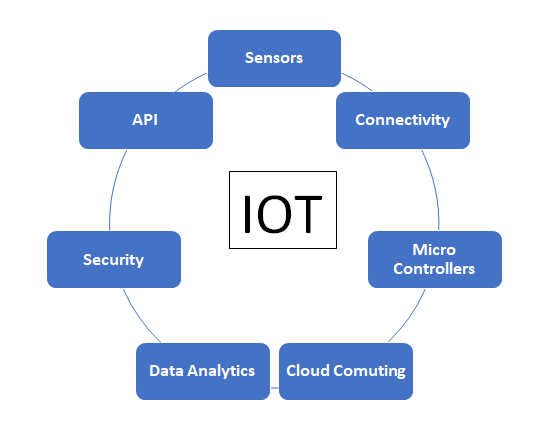
Building blocks for IOT
The building blocks of IoT are the components and technologies that make it possible for devices to communicate and exchange data over the internet. Here are some of the key building blocks for IoT:
- Sensors: These are devices that detect and measure physical parameters such as temperature, humidity, pressureand light. Sensors are a critical component of IoT because they provide the data that enables devices to respond to changes in the environment.
- Connectivity: IoT devices need to be able to connect to the internet to exchange data with other devices and cloud services. There are several connectivity options available for IoT devices, including Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, cellular, and satellite.
- Microcontrollers: These are small computers that are used to control and manage IoT devices. Microcontrollers are typically low-power and low-cost, making them ideal for use in embedded systems.
- Cloud computing: The cloud is used to store and process the data collected by IoT devices. Cloud computing enables IoT devices to offload compute and storage requirements, providing scalability and flexibility for IoT applications.
- Data analytics: IoT generates a vast amount of data, and data analytics is used to make sense of this data. Machine learning and AI are used to identify patterns and insights from the data, enabling organizations to make informed decisions.
- Security: IoT devices are vulnerable to cyber attacks, and security is a critical concern for IoT applications. Security measures include encryption, authentication, and access control, among others.
- Application programming interfaces (APIs): APIs are used to enable IoT devices and applications to communicate with each other. APIs provide a standardized way for different devices and applications to exchange data and services, enabling interoperability and integration.